How does Dong Quai Tea bags fertility?
 2025-08-19 16:50:04
2025-08-19 16:50:04
What is angelica sinensis ?
Dong Quai Tea bags(also known as dried angelica, Qinna, western angelica, Min angelica, golden angelica, angelica root, han angelica tail, angelica koji, and wild angelica) is a perennial herb, 0.4-1 meter tall. It blooms from June to July, and fruiting occurs from July to September. European angelica was introduced to China in 1957. It is primarily produced in southeastern Gansu, with Minxian County boasting high yields and excellent quality. It is also cultivated in Yunnan, Sichuan, Shaanxi, and Hubei provinces. Some provinces across China have also introduced and cultivated it. Its root is used medicinally and is one of the most commonly used traditional Chinese medicines. It has the benefits of nourishing and regulating blood circulation, regulating menstruation and relieving pain, moisturizing the intestines, and promoting anti-aging and immunity. Meanwhile, angelica sinensis is good for fertility.

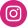
Appearance of Dong Quai Tea bags
Angelica sinensis is 0.4-1 m tall perennial herb. The terete, branched root has numerous yellow-brown fleshy fibrous roots and has strong odour. Smooth, glabrous stem is erect, purplish or greenish-white, and profoundly grooved.
The petioles 3-11 cm long are swollen at base into tubular, membranous sheaths that are purple or green. Ternate leaves are two to three times pinnate-lobed. Basal leaves and lower stem leaves are ovate in form, 8-18 cm long and 15-20 cm wide. There are three pairs of leaflets, petioles of lower pair 0.5-1.5 cm long, lower pair being sessile. Terminal lobes are ovate or ovate-lanceolate, 1-2 cm long and 5-15 mm wide, 2-3 shallowly lobed, with notched, serrate margins and pointed tips. The margins and lower surface of leaves are sparsely covered with fine papillate white hairs. Upper stem leaves are narrowed to sac-like sheaths and pinnate-lobed leaves.
Compound umbel inflorescence, with a densely pubescent peduncle 4-7 cm long; 9-30 rays; 2 linear or absent bracts; 13-36 umbels; 2-4 linear bracts; white flowers; densely pubescent pedicels; 5 ovate calyx teeth; oblong ovate petals, narrowly pointed at the apex, inflexed; short style with a conical stylobase. Flowering period: 6-7 months.
Fruit: elliptical to ovate, 4-6 mm long, 3-4 mm wide, with a linear, raised dorsal ridge and lateral ridges forming broad, thin wings, as wide as or slightly wider than the fruit body. The wings have pale purple margins. One vittae is present in the furrow and two on the commissure. Fruiting period: July-September.
What is the benefits of angelica sinensis for fertility?
Angelica sinensis is a universally used herb in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) gynecology and is referred to as the "Holy Blood Medicine." It benefits female reproductive health primarily by:
1. Regulating Menstruation and Fertility
Activating Blood and Regulating Menstruation
Danggui activates blood and regulates menstruation to relieve menstrual irregularities caused by stasis of blood (e.g., delayed menstruation, dark purple blood with clots during menstruation), and promotes conception by improving the uterine microenvironment.
The classic formula: Siwu Decoction (Danggui, Chuanxiong, White Peony Root, and Rehmannia Root) is a root formula for menstrual regulation.
Nourishing Blood and Nourishing the Uterus
With iron and vitamin B12 content, it is used for women with thin menstrual flow and pale face due to blood deficiency. It might enhance endometrial receptivity and boost embryo implantation rates.
2. Support Pregnancy and Postpartum Recovery
Angelica sinensisi feryility means tocolytic Effects (Requires Combination Use)
Combined with Scutellaria baicalensis and Atractylodes macrocephala (e.g., Danggui San), it can be used to treat fetal dyskin caused by blood deficiency. It must be given under the skilled care of an expert TCM physician, though, and not single or in large quantities.
Postpartum Recovery
Induces lochia expulsion and treats postpartum abdominal pain caused by deficiency of blood. Used with peach kernel and roasted ginger (e.g., Shenghua Tang), it is often utilized.

III. Regulating Endocrine and Ovarian Function
Phytoestrogenic Effects
Ferulic acid and other compounds in angelica may bidirectionally regulate estrogen levels, offering some supportive benefits for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or premature ovarian failure. Constitutional diagnosis must be employed together with this.
IV. Precautions and Contraindications
Use with Caution
Those with Yin deficiency and excess fire (hot flashes, dry mouth) or damp-heat constitution (yellow, greasy tongue coating) should reduce dosage or use concurrently with yin-nourishing herbs.
Prevent excessive menstrual loss or early pregnancy (first trimester) with angelica extract in high doses.
Modern Research Supplements
Animal studies have shown Dong Quai Tea bags to improve ovarian reserves' function, but clinical trials are pending from higher-quality trials.
V. Recommended Usage (Subject to individual adjustment)
Daily Use: Soak angelica 5-10 grams and wolfberry 10 grams in water (for blood deficiency patients, 2-3 times per week). Prescribed Medicinal Diet: Angelica, Ginger, and Lamb Soup (warms meridians and dispels cold, suitable for female patients to assist in conception during winter).
It is advisable to consult a practitioner of Traditional Chinese Medicine prior to use, and to combine with other herbs according to your constitution (e.g., deficiency of qi, stasis of blood, etc.) so as not to blindly augment tonics.
What are the undesirable effects of angelica sinensis?
1. Those with allergic constitutions should avoid using it.
2.Angelica sinensis is more likely to irritate the gastrointestinal tract in those with pre-existing gastrointestinal dysfunction.
3.Prolonged consumption of angelica sinensis will place a greater metabolic burden on the kidneys and disrupt kidney function. Therefore, avoid its long-term use to avoid deleterious health effects.
4. Impact on Blood Pressure
In some cases, angelica has an impact on blood pressure, like increasing or lowering it.5 Thus, patients suffering from conditions such as hypertension or any other cardiac disorder should take precautions when they consume angelica and do what the physician recommends.5
5. Stimulating Uterine Contractions
angelica sinensis possesses a blood-activating effect as well as uterine contraction, which poses a particularly dangerous risk to pregnant women. Particularly during early and late pregnancy, the use of angelica sinensis will result in miscarriage or premature birth. Therefore, angelica sinensis should not be consumed by pregnant women.
6. Influence on Fetal Development
angelica sinensis has a combined mixture of compounds, and certain of them can cross the placenta to the fetus. Although no one can be certain of the mechanism, it is possible to interfere with normal fetal growth and development. Pregnant women should therefore exercise extreme care in their use of angelica sinensis.
7. Other Adverse Reactions
Sleepiness or sleepiness are some of the side effects that others feel after consuming angelica sinensis, which normally resolves with cessation. Headache, fever, dry mouth, nausea after administration of angelica sinensis, which normally resolves with cessation.
In conclusion, even though angelica sinensis is wonderful in numerous ways, its potential side effects must be strictly considered when used, especially among individuals with allergy, pregnant women, and lactating mothers. It should only be taken under a doctor's recommendation.











_1750401612782.webp)

_1750230754233.webp)
_1744966358161.webp)
_1747382917845.webp)
_1753257511326.webp)

